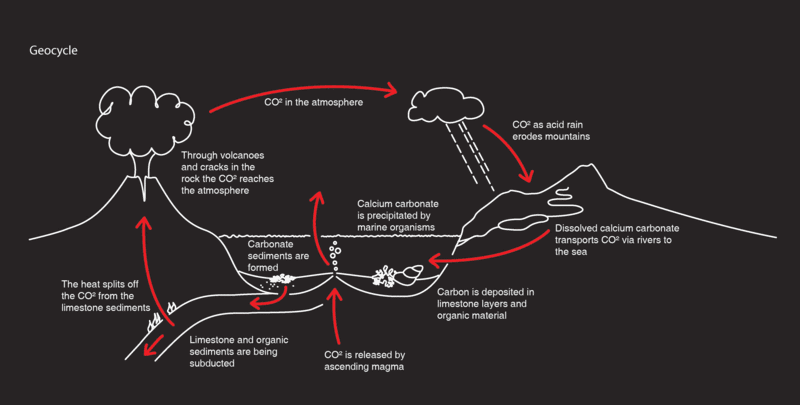
Carbon is the 4th most abundant element in the universe, and can form into more compounds than any other element. This is what makes it the basis of all the chemical reactions upon which life on earth is based. Next to oxygen, carbon forms the greatest part of a human body’s mass. No wonder the natural cycle of carbon reactions here on earth has become of such great importance. But the great range of carbon containing molecules also makes it extremely active in the long, slow process of the geochemistry of earth cycling with plate tectonics over many millions of years.
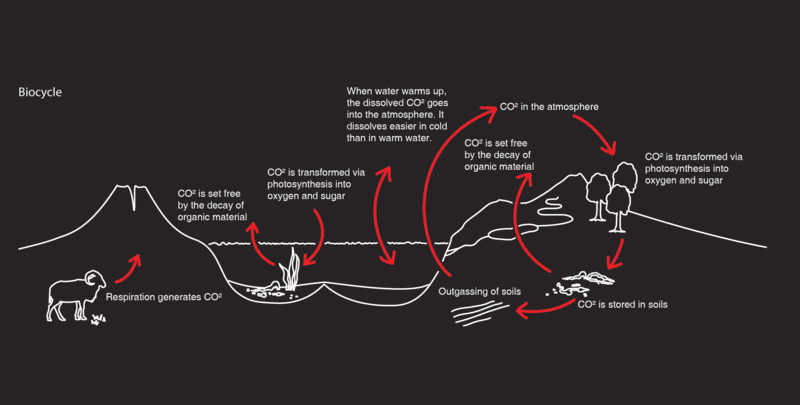
But there is a much faster carbon cycle based on the interactions in the biosphere of the earth: all the living things, plants, animals, bacterium and other micro-organisms that blanket the planet. Before the widespread use of fossil fuels, the composition of the atmosphere was balanced by this fast carbon cycle between CO2-absorbing, oxygen-producing plants, and CO2-producing, oxygen-absorbing animals as well as the microbes. It has not been in a steady equilibrium, but in a dynamic balance, with the relative levels cycling via various feedback effects, such as the green house effect which causes the temperature of the atmosphere to rise as the levels of CO2 rise, until a tipping point is reached in the balance.
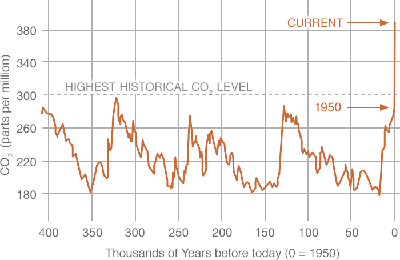
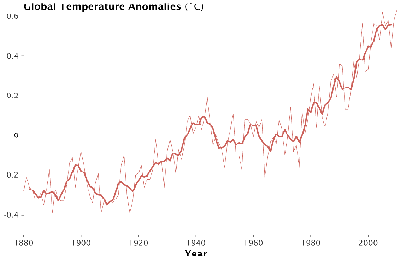
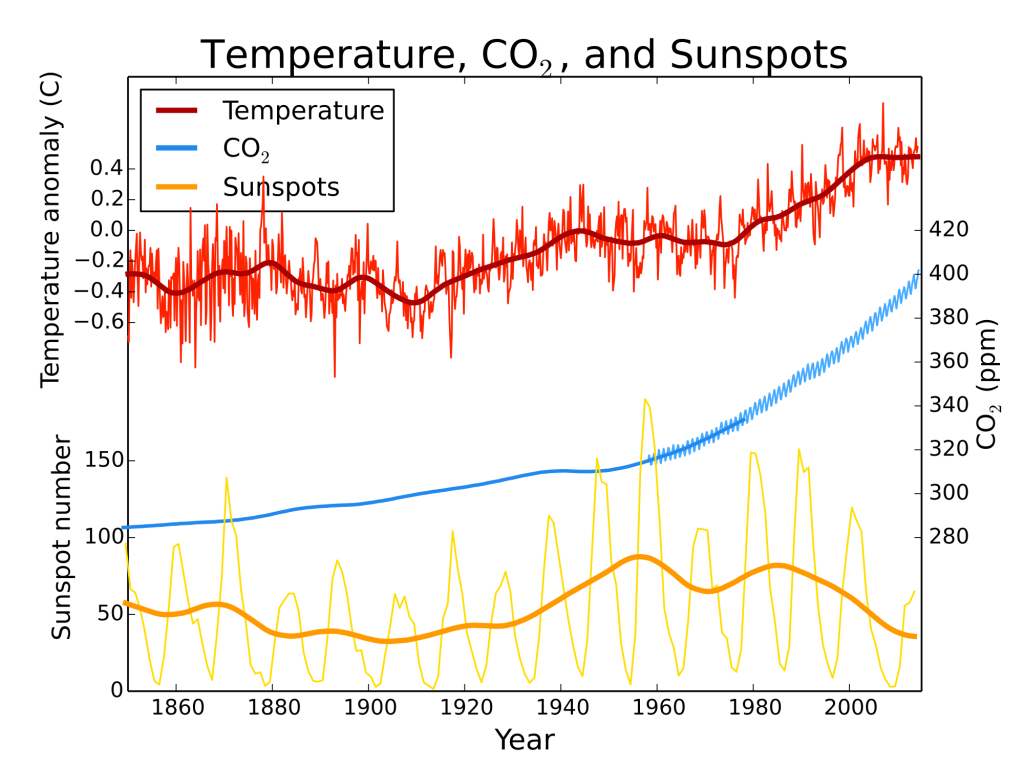
It was just this sort of correlation between temperature and CO2 concentrations that first alerted climate scientists to the possible consequences of the rising CO2 levels resulting from our industrialization as they saw global CO2 levels climbing to unprecedented levels in step with global temperatures.
But of course, correlation is not causation, and for this reason it has taken a number of decades and a lot of careful science to get to the consensus we have finally arrived at, that the natural cycle is being overwhelmed by the industrial cycle.
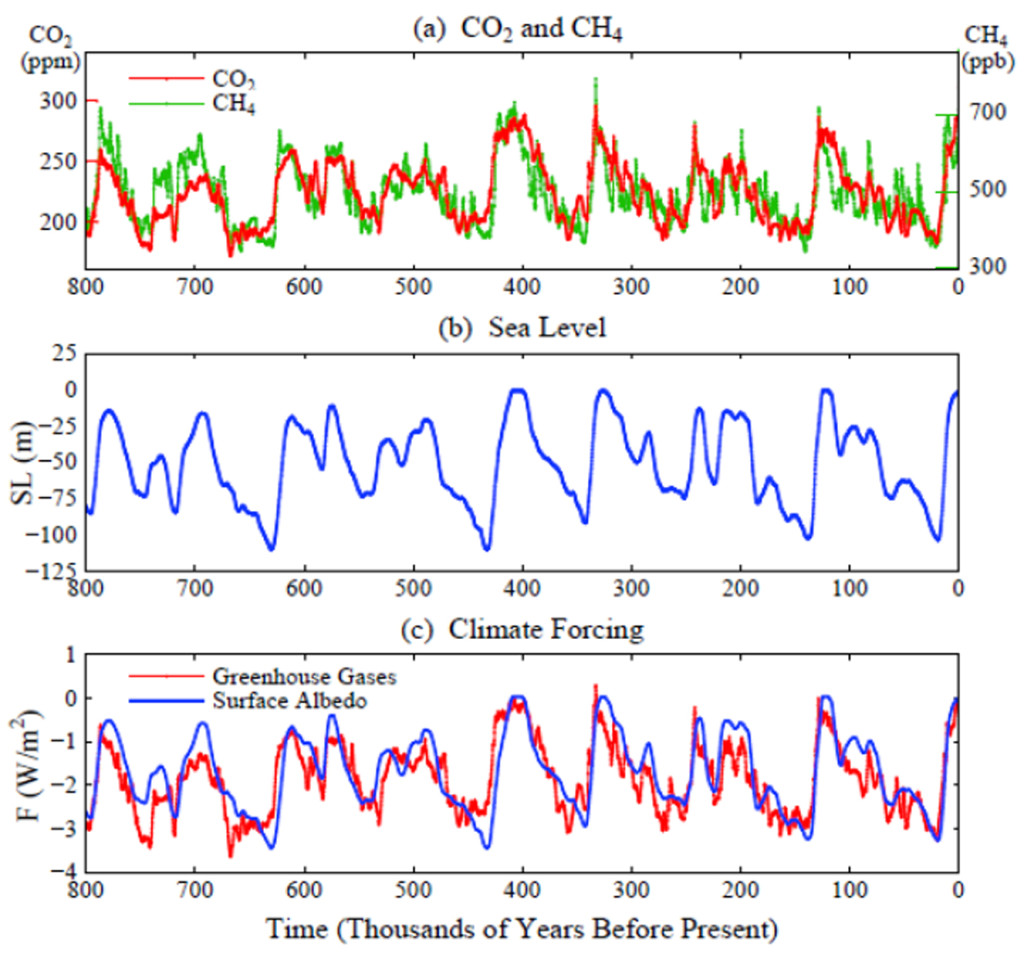
To be fair that cycle of temperature variation also closely tracks solar activity, which likely underlies the cycles of glaciation. The exact causes of this pattern of advancing and retreating glaciers that have characterized the last 100,000 or so years are not fully understood. These cycles are certainly related to changes in the insolence, or amount of energy the earth is receiving from the sun, but the climate is a complex system, and it is clear that these astronomical factors are all closely interrelated with these biological and atmospheric conditions.
In fact studies of our solar system’s neighboring rocky planets, Venus and Mars, have advanced our understanding of these global climate dynamics. While working with JPL on the biological detection experiments for the original Mars Viking Landers, James Lovelock proposed the ill-named Gaia Hypothesis, which while a victim of the teleological implications of the name, has resulted in a widespread scientific acceptance of more holistic understanding of the planet, and how its geology, soils, gases and biology are involved in an intricate web of feedback loops which serve to help stabilize our highly reactive atmosphere in a homeostasis suitable for life to persist.
Gaia continues to be misunderstood being cited by climate-change deniers as a process which will prevent the catastrophic climate change predicted by current modeling. Even if all its mechanisms are not fully understood, it is clear that its effects are too weak to compensate for the extreme imbalance in the system created by our industrialization under fossil fuels. The intimate and fragile inter-relation of all the earth’s systems has become undeniable, and addressing climate change in the context of these complex natural systems is imperative.